What are 6 pillars of iman – What are the Six Pillars of Iman? These six fundamental beliefs form the very core of Islamic faith, shaping the beliefs and practices of Muslims worldwide. Let’s delve into the essence of each pillar and explore their interconnectedness.
Belief in Allah, Angels, Holy Books, Prophets, the Day of Judgment, and Divine Decree – these pillars stand as the unshakeable foundation upon which the Muslim faith rests.
Iman as a Central Tenet of Islam
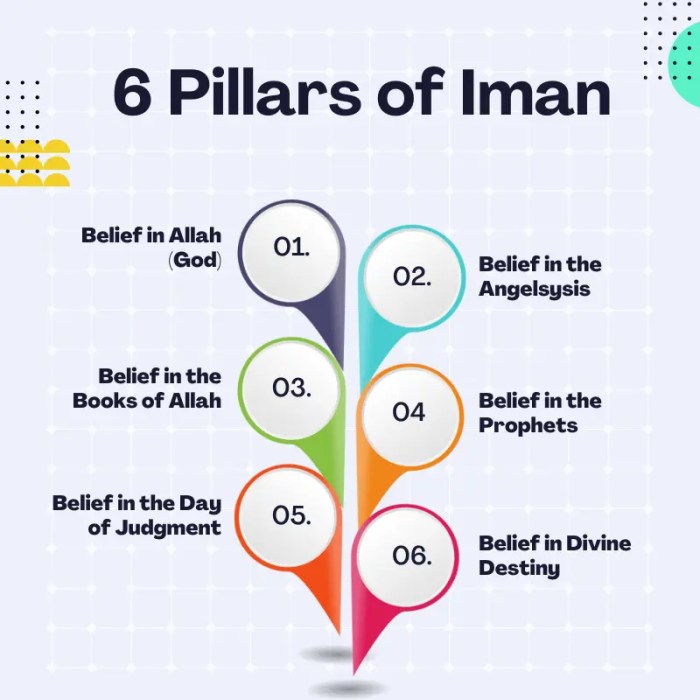
Iman is a fundamental concept in Islam, representing the core beliefs that shape the faith and guide the actions of Muslims. It encompasses faith in Allah (God), His prophets, His revealed books, the angels, the Day of Judgment, and divine destiny.
Iman serves as the foundation upon which Islamic practices and rituals are built.
The Significance of Iman
Iman plays a pivotal role in the lives of Muslims, providing them with a sense of purpose and direction. It shapes their moral compass, ethical conduct, and spiritual development. Iman instills a deep belief in Allah’s sovereignty, fostering gratitude, submission, and trust in His divine plan.
It encourages Muslims to strive for righteousness, to seek knowledge, and to engage in acts of worship that demonstrate their devotion and strengthen their connection with the Almighty.
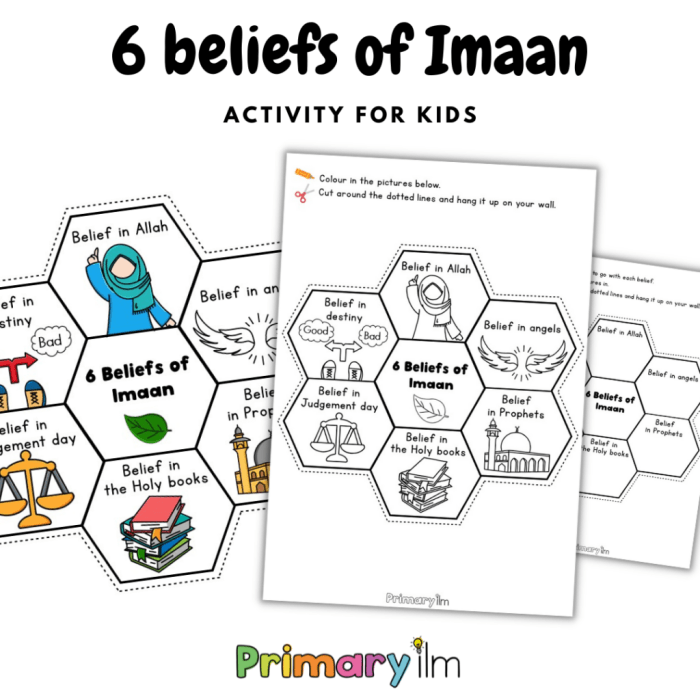
The Six Pillars of Iman
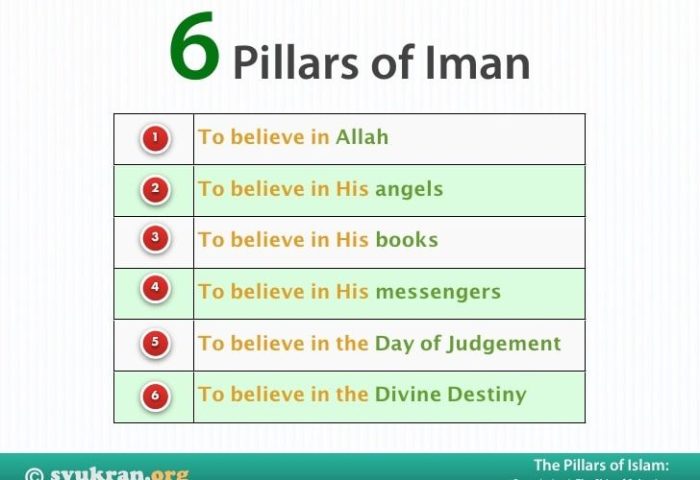
Iman, the central tenet of Islam, encompasses the belief in six fundamental pillars that shape the faith and guide the lives of Muslims. These pillars provide a comprehensive framework for understanding the core beliefs of Islam and establish the foundation upon which Muslims build their spiritual and moral lives.
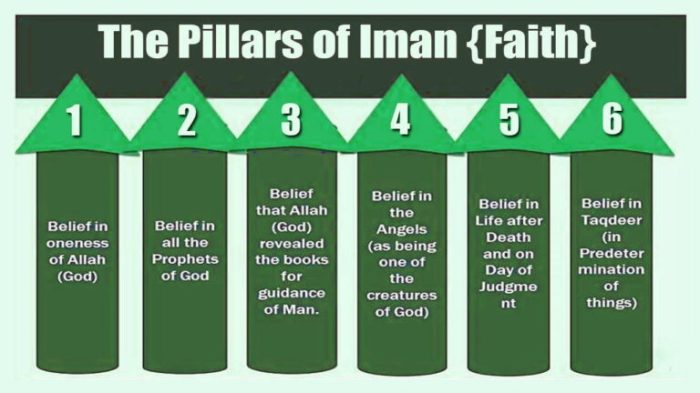
The six pillars of iman, or faith, are the foundation of Islam. They include belief in Allah, His angels, His books, His prophets, the Day of Judgment, and divine decree. These pillars provide a framework for understanding the world and our place in it.
While different cultures may have different ways of expressing their faith, the core beliefs of Islam remain the same. Just like how the “way in China crossword” may be different from other crosswords, the essence of the puzzle remains the same.
Belief in Allah
The first pillar of iman is the belief in the existence and oneness of Allah, the one and only God. Muslims believe that Allah is the creator and sustainer of the universe, the source of all wisdom and knowledge, and the ultimate judge of all actions.
Belief in Angels
The second pillar of iman is the belief in angels, celestial beings created by Allah to serve as His messengers and intermediaries between Him and humankind. Muslims believe that angels are pure and obedient creatures, each with specific duties and responsibilities, such as recording deeds, protecting believers, and conveying divine messages.
Belief in Holy Books
The third pillar of iman is the belief in holy books revealed by Allah to guide humanity. Muslims believe that the Quran is the final and most complete revelation, containing the divine word of Allah and providing guidance for all aspects of life.
Other holy books, such as the Torah and the Gospel, are also recognized as divinely inspired scriptures that convey Allah’s message.
Belief in Prophets
The fourth pillar of iman is the belief in prophets, chosen individuals sent by Allah to guide and teach humankind. Muslims believe that Muhammad is the final and greatest prophet, sent to deliver the Quran and complete the divine message.
Other prophets, such as Abraham, Moses, and Jesus, are also revered as messengers of Allah.
Belief in the Day of Judgment
The fifth pillar of iman is the belief in the Day of Judgment, when all humans will be resurrected and held accountable for their actions in this life. Muslims believe that on this day, Allah will judge each person based on their beliefs and deeds, determining their eternal destiny in heaven or hell.
Belief in Divine Decree
The sixth pillar of iman is the belief in divine decree, the concept that everything that happens in the universe is ultimately determined by Allah’s will. Muslims believe that while humans have free will, Allah has knowledge of all things and has predetermined the outcome of all events.
The Interconnectedness of the Pillars
The six pillars of iman are not isolated concepts; they are deeply interconnected and interdependent. Each pillar supports and strengthens the others, forming a cohesive framework for a believer’s faith.
For instance, belief in Allah (the first pillar) provides the foundation for the remaining pillars. Without this belief, the other pillars would lack meaning and purpose. Belief in the angels (the second pillar) reinforces the first pillar by acknowledging the existence of beings who carry out Allah’s commands and witness human actions.
The Interdependence of the Pillars
- Belief in the prophets (the third pillar) is crucial for understanding the teachings and guidance that Allah has revealed through them. It strengthens the belief in Allah and His attributes.
- Belief in the revealed books (the fourth pillar) provides a written record of Allah’s teachings, which guides believers in their daily lives and helps them distinguish right from wrong.
- Belief in the Day of Judgment (the fifth pillar) instills a sense of accountability and encourages believers to live righteous lives. It reinforces the importance of good deeds and warns against evil.
- Belief in divine decree (the sixth pillar) acknowledges that Allah is the ultimate controller of all events and outcomes. It fosters a sense of contentment and acceptance of one’s fate.
The Practical Implications of Iman: What Are 6 Pillars Of Iman

Iman, the unwavering belief in the tenets of Islam, holds profound significance in the daily lives of Muslims. It serves as a guiding force, shaping their actions, decisions, and relationships. Through its practical implications, iman becomes an integral part of the fabric of Muslim existence.
Firstly, iman instills a sense of accountability and responsibility. Muslims believe that Allah is ever-present and aware of their deeds. This awareness prompts them to act righteously, striving to live in accordance with Islamic principles. Iman motivates them to fulfill their obligations, such as prayer, fasting, and charity, with sincerity and devotion.
Moral and Ethical Compass
Iman serves as a moral and ethical compass, guiding Muslims in their interactions with others. It emphasizes the importance of honesty, integrity, and justice. Muslims are taught to treat others with respect, regardless of their background or beliefs. Iman encourages them to promote peace, harmony, and cooperation within society.
Patience and Perseverance
Iman fosters patience and perseverance in the face of challenges. Muslims believe that difficulties are part of life’s test, and that by enduring them with faith, they will ultimately reap rewards. Iman provides solace during times of adversity, reminding Muslims that they are not alone and that Allah is always with them.
Contentment and Gratitude
Iman cultivates contentment and gratitude. Muslims recognize that everything they have comes from Allah, and they are grateful for His blessings. Iman helps them appreciate the simple joys of life and to find contentment in what they possess. It also encourages them to share their blessings with others, promoting a spirit of generosity and compassion.
Hope and Optimism
Iman instills hope and optimism in the hearts of Muslims. They believe that even in the darkest of times, there is always light at the end of the tunnel. Iman reminds them that Allah is merciful and forgiving, and that with His help, they can overcome any obstacle.
It encourages them to remain positive and to strive for a better future.
In summary, iman has far-reaching practical implications in the lives of Muslims. It guides their actions, shapes their decisions, and fosters ethical behavior. Iman provides solace during challenges, cultivates contentment, and instills hope. By embracing iman, Muslims strive to live meaningful and fulfilling lives, in accordance with the teachings of Islam.
Strengthening Iman
Strengthening one’s iman is a lifelong journey that requires dedication and perseverance. Here are some practices and rituals that can help Muslims enhance their faith:
Prayer (Salah)
- Performing the five daily prayers with sincerity and devotion.
- Understanding the meanings and supplications in the prayers.
- Making extra prayers, such as Tahajjud and Dhuha.
Reading the Quran
- Reciting the Quran regularly, even if it’s just a few verses.
- Contemplating the meanings and messages of the Quran.
- Attending Quran classes or listening to tafsir (Quranic exegesis).
Remembrance (Dhikr), What are 6 pillars of iman
- Constantly remembering Allah through ذکر (dhikr) and glorifying Him.
- Making use of prayer beads (tasbih) to count dhikr.
- Incorporating dhikr into daily activities, such as driving or working.
Supplication (Dua)
- Making sincere supplications to Allah, seeking His guidance and assistance.
- Using specific supplications for strengthening iman, such as “Ya Muqallibul-qulub, thabbit qalbi ala dinik” (O Turner of hearts, make my heart firm upon Your religion).
- Being persistent in dua, even when answers are not immediately apparent.
Seeking Knowledge
- Studying Islamic teachings from reliable sources.
- Attending lectures, workshops, and seminars on Islam.
- Engaging in discussions and debates about Islamic topics with respect and open-mindedness.
Company of the Righteous
- Surrounding oneself with people who inspire and encourage iman.
- Joining Muslim communities and organizations.
- Seeking the guidance of scholars and spiritual leaders.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the significance of the Six Pillars of Iman?
They form the foundation of Islamic faith and shape the beliefs and practices of Muslims.
How are the Six Pillars of Iman interconnected?
Each pillar supports and strengthens the others, creating a cohesive and interdependent system of belief.