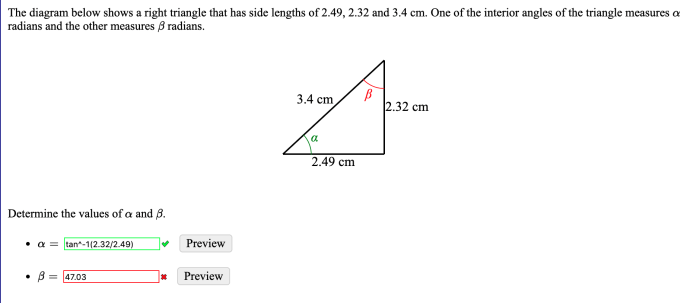
Embark on a mathematical odyssey with Unit 11 Volume and Surface Area Homework 4, where the enigmatic realm of prisms, pyramids, cones, and cylinders unveils its secrets. Delve into the depths of geometry as we unravel the mysteries of volume and surface area, deciphering the intricate relationships between dimensions and spatial properties.
Prepare to witness the interplay of mathematical formulas and real-world applications, as we explore the practical significance of volume and surface area in our everyday lives. From the towering pyramids of ancient civilizations to the sleek contours of modern architecture, this homework assignment illuminates the fundamental role of geometry in shaping our world.
Volume and Surface Area
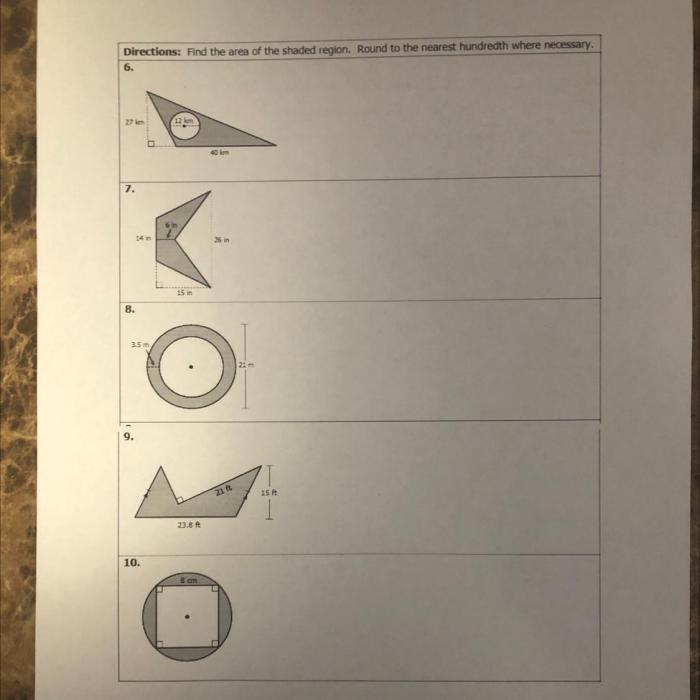
Volume and surface area are two important concepts in geometry that are used to measure the size and shape of objects. Volume is a measure of the amount of space that an object occupies, while surface area is a measure of the total area of the surfaces of an object.
Volume of Prisms and Cylinders
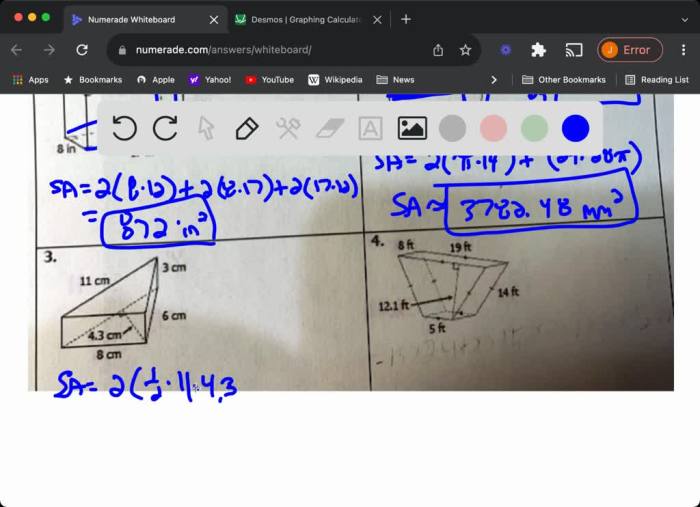
A prism is a three-dimensional shape with two parallel bases that are congruent polygons. The volume of a prism is calculated by multiplying the area of the base by the height of the prism.
A cylinder is a three-dimensional shape with two parallel circular bases. The volume of a cylinder is calculated by multiplying the area of the base by the height of the cylinder.
Example: Calculating the Volume of a Rectangular Prism
A rectangular prism has a length of 5 cm, a width of 3 cm, and a height of 2 cm. The volume of the prism is calculated as follows:
Volume = Length × Width × Height
Volume = 5 cm × 3 cm × 2 cm
Volume = 30 cm³
Relationship between Volume and Dimensions of a Prism
The volume of a prism is directly proportional to the area of the base and the height of the prism. This means that if the area of the base or the height of the prism is increased, the volume of the prism will also increase.
Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders: Unit 11 Volume And Surface Area Homework 4
The surface area of a prism is the sum of the areas of all of its faces. The surface area of a cylinder is the sum of the areas of the two circular bases and the lateral surface area.
Example: Calculating the Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism, Unit 11 volume and surface area homework 4
A rectangular prism has a length of 5 cm, a width of 3 cm, and a height of 2 cm. The surface area of the prism is calculated as follows:
Surface Area = 2(Length × Width + Width × Height + Height × Length)
Surface Area = 2(5 cm × 3 cm + 3 cm × 2 cm + 2 cm × 5 cm)
Surface Area = 54 cm²
Relationship between Surface Area and Dimensions of a Prism
The surface area of a prism is directly proportional to the area of the base and the height of the prism. This means that if the area of the base or the height of the prism is increased, the surface area of the prism will also increase.
Detailed FAQs
What is the formula for calculating the volume of a rectangular prism?
Volume = length × width × height
How is the surface area of a prism related to its dimensions?
Surface Area = 2(length × width + width × height + height × length)
What is the significance of volume and surface area in real-world applications?
Volume and surface area play crucial roles in fields such as architecture, engineering, and packaging, enabling us to optimize space, design structures, and determine the efficiency of containers.