Self tapping screws are primarily used when fastening objects to – Self-tapping screws are primarily used when fastening objects to a variety of materials, offering a convenient and versatile solution for a wide range of applications. Their unique design eliminates the need for pre-tapping, making them a popular choice for both DIY enthusiasts and professionals.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of self-tapping screws, exploring their applications, materials, sizes, and types. We will also provide detailed installation considerations and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using these screws. Additionally, we will examine alternative fastening methods and provide guidelines for designing applications that involve the use of self-tapping screws.
Overview of Self-Tapping Screws
Self-tapping screws, also known as self-threading screws, are fasteners specifically designed to create their own thread as they are driven into a material. Unlike traditional screws, which require a pre-drilled hole, self-tapping screws can be directly inserted into the workpiece, eliminating the need for additional steps.
These screws feature a sharp point and cutting threads that engage with the material as they are turned, forming a strong and secure connection. They are commonly used in applications where it is impractical or impossible to pre-drill holes, such as thin metal sheets, plastics, and softwoods.
Applications of Self-Tapping Screws
Self-tapping screws are widely used across various industries and sectors, including:
- Construction: Assembling metal roofing, framing, and other building components
- Automotive: Securing body panels, interior trim, and electrical components
- Electronics: Fastening circuit boards, heat sinks, and other electronic devices
- Manufacturing: Assembling machinery, appliances, and other industrial products
- DIY and home improvement: Installing shelves, hanging pictures, and performing various repairs
Materials and Finishes
Self-tapping screws are typically manufactured from:
- Steel: Provides strength and durability
- Stainless steel: Resists corrosion and rust
- Brass: Offers corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity
- Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant
Various finishes are available to enhance screw performance and durability, including:
- Zinc-plated: Provides basic corrosion resistance
- Chromate-plated: Improves corrosion resistance and wear resistance
- Nickel-plated: Offers a bright, decorative finish with good corrosion resistance
- Black oxide: Provides a dark, protective finish
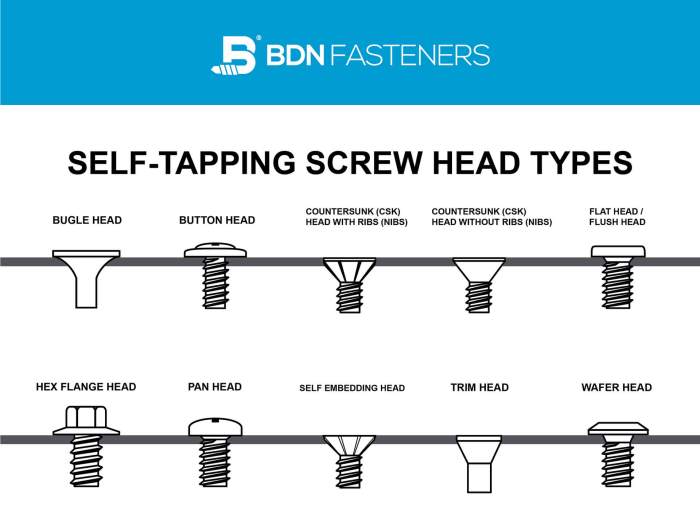
Sizes and Types
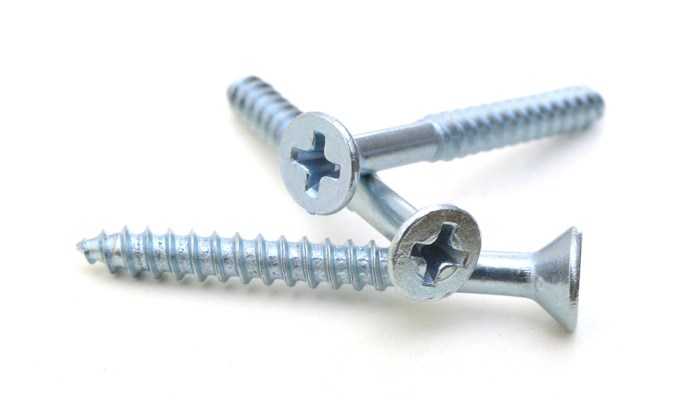

Self-tapping screws are available in a wide range of sizes, from small screws used in electronics to large screws used in construction. They are commonly classified by their:
- Diameter: Measured in inches or millimeters
- Length: Measured from the tip to the head
Various types of self-tapping screws exist, including:
- Pan head: Round head with a flat top
- Hex head: Hexagonal head that allows for tightening with a wrench
- Truss head: Low-profile head with a slightly rounded top
- Wafer head: Very thin head designed for flush mounting
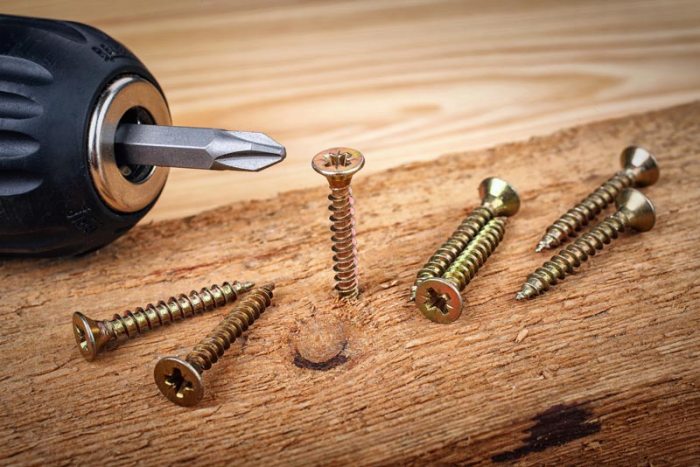
Installation Considerations
To ensure proper installation of self-tapping screws, it is important to:
- Use a pilot hole: Pre-drilling a pilot hole slightly smaller than the screw diameter helps prevent material damage and ensures smooth insertion.
- Select the appropriate screw size: Choosing the correct screw size based on the material thickness and load requirements is crucial.
- Use the right tools: Using a screwdriver or drill with the appropriate bit size and torque settings is essential.
- Tighten properly: Over-tightening can damage the screw or material, while under-tightening can lead to a loose connection.
Advantages and Disadvantages

Self-tapping screws offer several advantages:
- Ease of installation: Eliminates the need for pre-drilling holes, saving time and effort.
- Versatility: Can be used in various materials, including metal, plastic, and wood.
- Strength and durability: Provide a secure connection that can withstand significant loads.
However, they also have some disadvantages:
- Potential for material damage: If installed improperly, self-tapping screws can damage the material they are being inserted into.
- Limited reusability: Once a self-tapping screw is removed, it may not be possible to reuse it in the same hole.
- Cost: Self-tapping screws can be more expensive than traditional screws.
Alternatives to Self-Tapping Screws: Self Tapping Screws Are Primarily Used When Fastening Objects To
In some cases, alternative fastening methods can be used instead of self-tapping screws, such as:
- Machine screws: Require a pre-tapped hole but offer higher strength and precision.
- Sheet metal screws: Designed for thin metal sheets and feature a self-piercing point.
- Rivets: Permanent fastening method that involves joining two pieces of material without the need for threads.
- Adhesives: Bonding agents that can provide a strong connection without the use of screws or bolts.
Design Considerations

When designing applications that involve the use of self-tapping screws, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Material properties: The type of material being fastened will determine the appropriate screw size, type, and finish.
- Load requirements: The strength of the screw should be sufficient to withstand the anticipated loads.
- Installation environment: Factors such as temperature, vibration, and corrosion should be taken into account when selecting the screw material and finish.
- Aesthetics: The type of screw head and finish can affect the appearance of the final product.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the advantages of using self-tapping screws?
Self-tapping screws offer several advantages, including ease of installation, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. They eliminate the need for pre-tapping, saving time and effort. Their ability to tap their own threads allows them to be used in a wide range of materials, including metal, plastic, and wood.
What are the different types of self-tapping screws?
There are various types of self-tapping screws available, including pan head, hex head, and flat head screws. Each type is designed for specific applications and materials. Pan head screws have a rounded head and are commonly used for general-purpose applications.
Hex head screws have a hexagonal head and are suitable for high-torque applications. Flat head screws have a countersunk head and are ideal for applications where a flush finish is desired.
How do I install self-tapping screws?
Installing self-tapping screws is relatively straightforward. However, it is important to choose the correct screw size and type for your application. It is also recommended to use a pilot hole to prevent the screw from breaking or stripping. To install the screw, simply insert it into the pilot hole and turn it clockwise until it is snug.