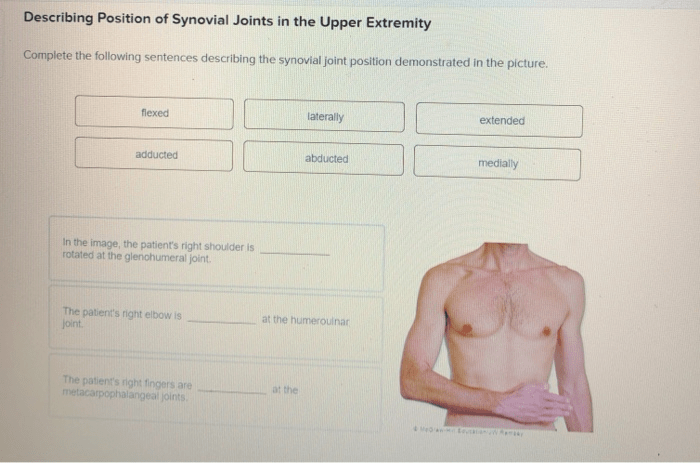
Complete the sentences describing the structure of a synovial joint. Synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the human body. They are characterized by their smooth, gliding surfaces and their ability to move freely. The structure of a synovial joint is complex, but it can be broken down into several key components.
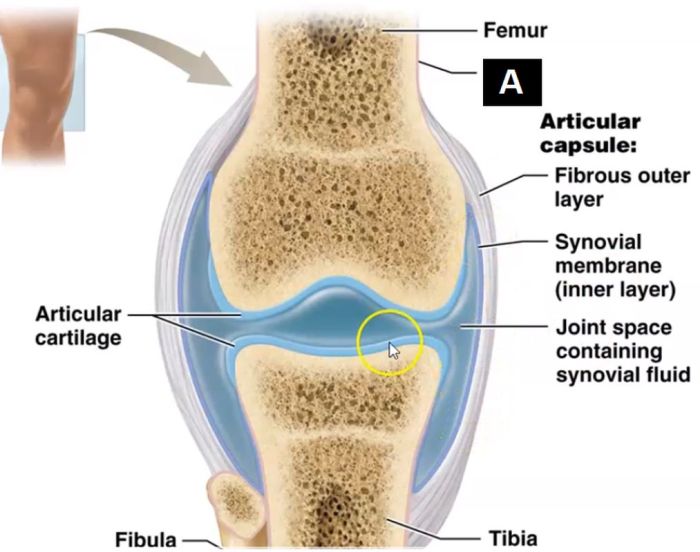
The articular cartilage is a layer of smooth, white tissue that covers the ends of the bones that form the joint. It helps to reduce friction and absorb shock. The synovial membrane is a thin layer of tissue that lines the joint capsule.
It produces synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint and nourishes the articular cartilage.
Structure of a Synovial Joint
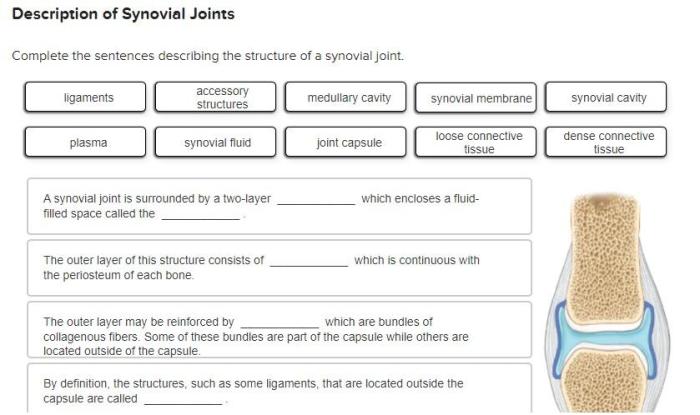
A synovial joint is a freely movable joint that allows for a wide range of motion. It is composed of several key components, including articular cartilage, synovial membrane, synovial fluid, joint capsule, ligaments, bursae, tendons, and blood vessels and nerves.
Articular Cartilage
Articular cartilage is a thin layer of smooth, white tissue that covers the ends of bones at the joint. It is composed of specialized cells called chondrocytes, which produce a matrix of collagen and proteoglycans. This matrix provides the cartilage with its strength and resilience.
Articular cartilage plays several important roles in the joint. It reduces friction between the bones, allowing them to move smoothly against each other. It also absorbs shock and protects the bones from damage.
Synovial Membrane
The synovial membrane is a thin, vascularized tissue that lines the joint capsule. It produces synovial fluid, which nourishes and lubricates the joint.
Synovial Fluid, Complete the sentences describing the structure of a synovial joint
Synovial fluid is a clear, viscous fluid that fills the joint cavity. It is composed of water, proteins, and hyaluronic acid. Hyaluronic acid gives synovial fluid its lubricating properties.
Synovial fluid plays several important roles in the joint. It lubricates the joint, reducing friction between the bones. It also nourishes the articular cartilage and provides nutrients to the cells in the joint.
Joint Capsule
The joint capsule is a tough, fibrous membrane that surrounds the joint. It is composed of two layers: the outer fibrous layer and the inner synovial layer.
The joint capsule plays several important roles in the joint. It encloses the joint, providing stability and support. It also prevents the joint from overextending or dislocating.
Ligaments
Ligaments are tough, fibrous bands of tissue that connect bones to each other. They are located outside the joint capsule.
Ligaments play several important roles in the joint. They stabilize the joint, preventing it from moving in abnormal directions. They also limit the range of motion of the joint.
Bursae and Tendons
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that are located between tendons and bones or between muscles and bones. They reduce friction between these structures.
Tendons are tough, fibrous cords of tissue that connect muscles to bones. They allow muscles to exert force on bones, causing movement.
Blood Supply and Innervation
Synovial joints are supplied with blood by arteries that enter the joint through the joint capsule. The nerves that innervate the joint provide sensation to the joint and its surrounding structures.
The blood supply and innervation of synovial joints are essential for their proper function. The blood supply provides nutrients to the cells in the joint, while the nerves provide sensation to the joint and its surrounding structures.
Types of Synovial Joints
There are six types of synovial joints:
- Plane joints
- Hinge joints
- Pivot joints
- Condyloid joints
- Saddle joints
- Ball-and-socket joints
Each type of synovial joint has a unique structure and range of motion.
FAQ Summary: Complete The Sentences Describing The Structure Of A Synovial Joint
What is the function of articular cartilage?
Articular cartilage helps to reduce friction and absorb shock.
What is the function of the synovial membrane?
The synovial membrane produces synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint and nourishes the articular cartilage.
What is the function of synovial fluid?
Synovial fluid lubricates the joint and nourishes the articular cartilage.
What is the function of the joint capsule?
The joint capsule encloses the joint and provides stability.
What is the function of ligaments?
Ligaments stabilize and limit joint movement.
What is the function of bursae and tendons?
Bursae and tendons reduce friction and facilitate movement.